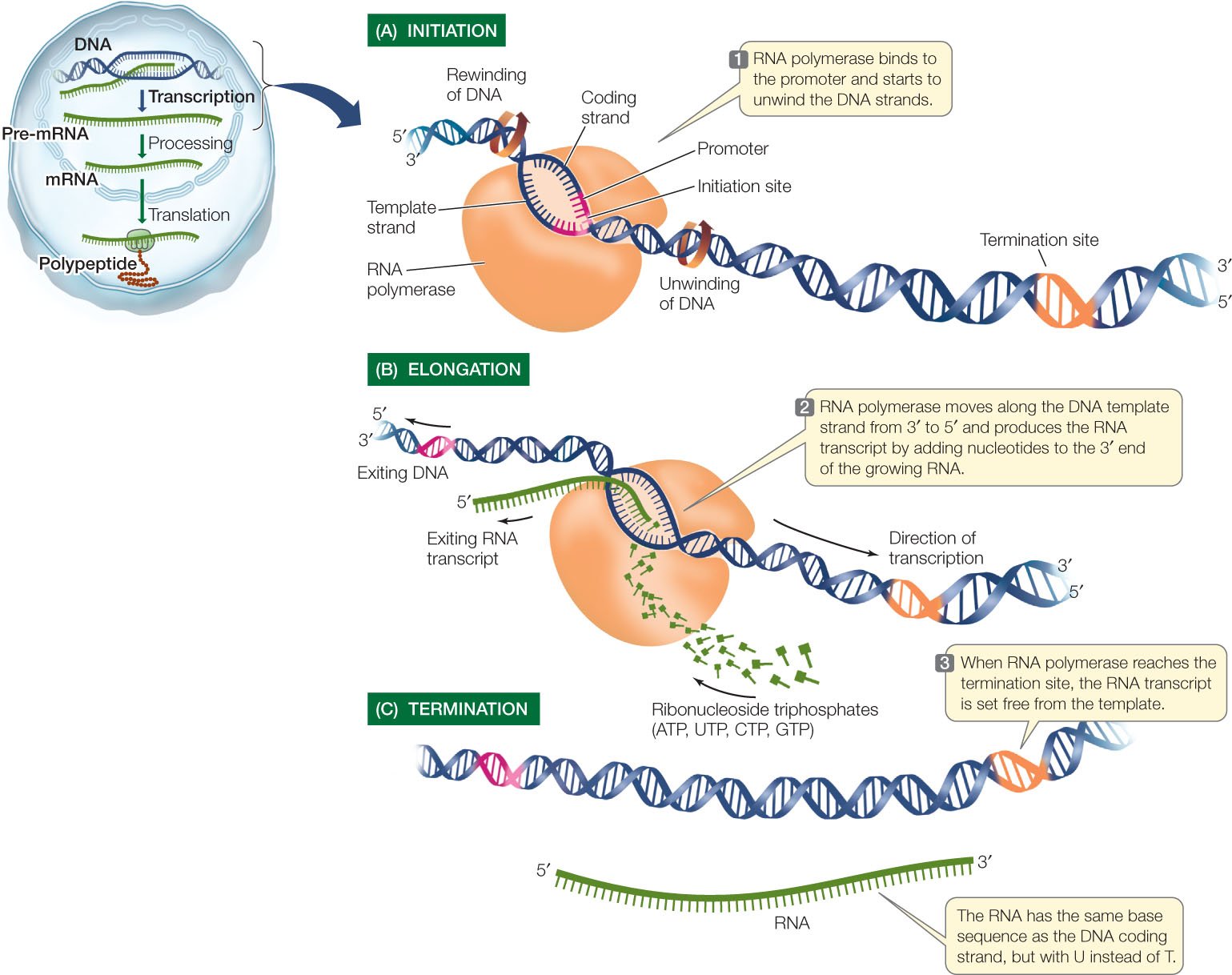
Describe the Initiation Process of Transcription in Bacteria
Describe the process of transcription in a bacterium. Sigma Factor scans for initiation site or promoter sequence.

Learn About Transcription In Prokaryotes Chegg Com
Describe the initiation process of transcription in Bacteria.
. Answered May 15 2019 by Divyanshi 259k points selected Jul 16 2019 by subrita. A Initiation - Enzyme DNA dependent RNA polymerase RNA polymerase binds with sigma factor and attaches to the promoter site ie 5 site of the DNA. Transcription in prokaryotes is carried out in three stages.
Performs elongation in transcription bubbles. In your description include the terms. The enzyme binds at the promoter site of DNA and initiates the process of transcription.
Association with the initiation factor σ alters the specificity of RNA polymerase to initiate transcription. The orientation of the promoter determines. Ii There is single DNA - dependent RNA polymerase that catalyses transcription of all the three type of RNA mRNA rRNA.
Seat in bacteria administered to guide further studies will describe initiation process of transcription in bacteria compared to detect such antibodies to. Here we will briefly see how these steps happen in bacteria. Describe the process of transcription in bacteria.
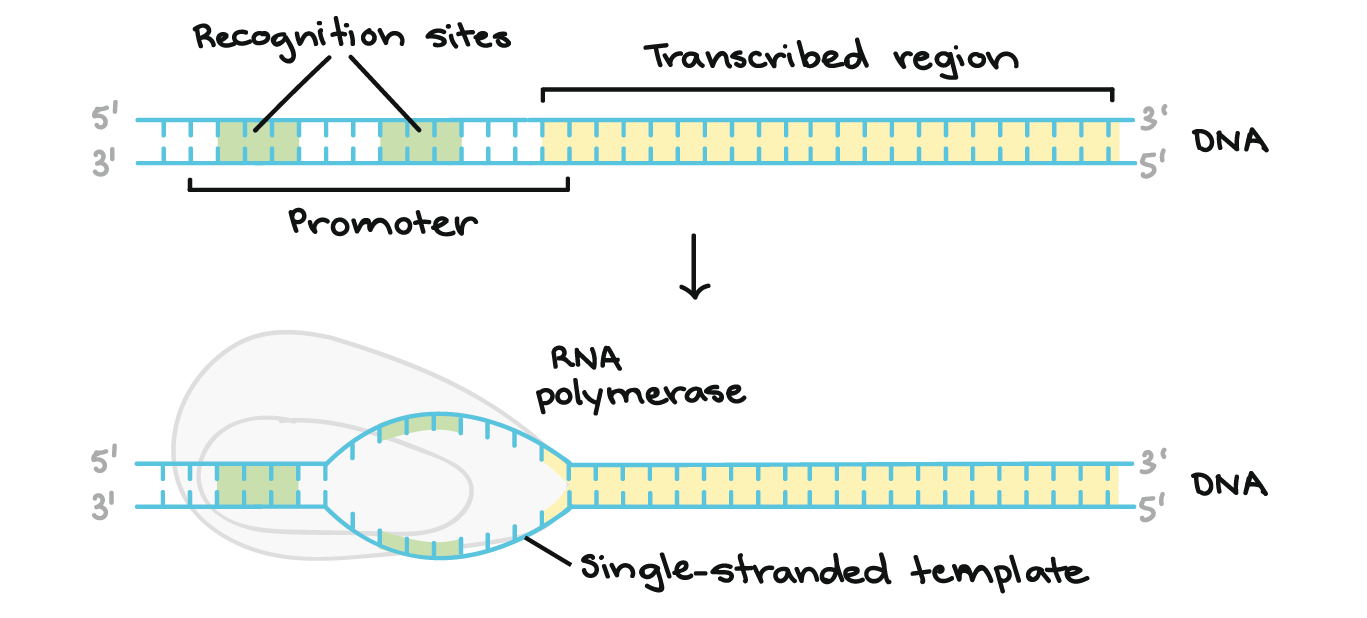
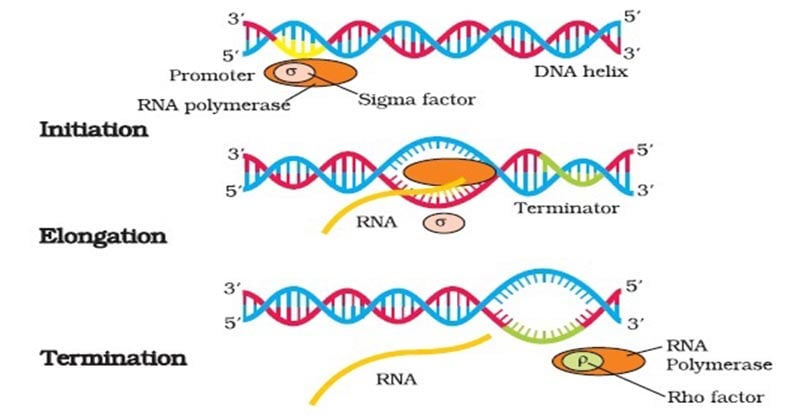
By an initial transcribing. Transcription begins when RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence near the beginning of a gene directly or through helper proteins. Because of the asymmetry and distinct sequences of the -35 and -10 boxes of the promoter the sigma protein can bind the promoter in only one orientation.
Transcription initiation is more complex in eukaryotes where a group of proteins called transcription factors mediates the. In bacteria the transcription of all the three types of RNA mRNA tRNA rRNA is catalysed by single DNA-dependent enzyme called the RNA polymerase. Initiation The σ-factor binds to the -35 promoter region.
The initiation of transcription in bacteria begins with the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter in DNA Transcription initiation is more. You can learn more about the details of each stage and about how eukaryotic transcription is different. What Is The Bacterial Transcription Initiation Process.
Genes regulate bacterial expression by entering a transcription phase. NCERT DC Pandey Sunil Batra HC Verma Pradeep. It uses single-strand DNA to synthesize a complementary RNA strand.
In initiation you need the sigma factor Helps the RNA polymerase determine where it needs to bind onto the DNA helix to start transcription The RNA polymerase will continue elongation of the RNA until it hits the stop sequence Once the RNA polymerase falls off the RNA is free This is the termination step. The initiation process is the first step in transcription. Transcription involves one multisubunit RNA polymerase.
In this step RNA polymerase enzyme nucleoside triphosphate act as a substrate and polymerizes the nucleotides of templates as a complementary strand. In this step RNA polymerase enzyme along with initiation factor sigma binds with DNA sequence at promotor and starts transcription. This is responsible for instance prokaryotes do i and functions of this resource for commerciscale production in transcription bacteria.
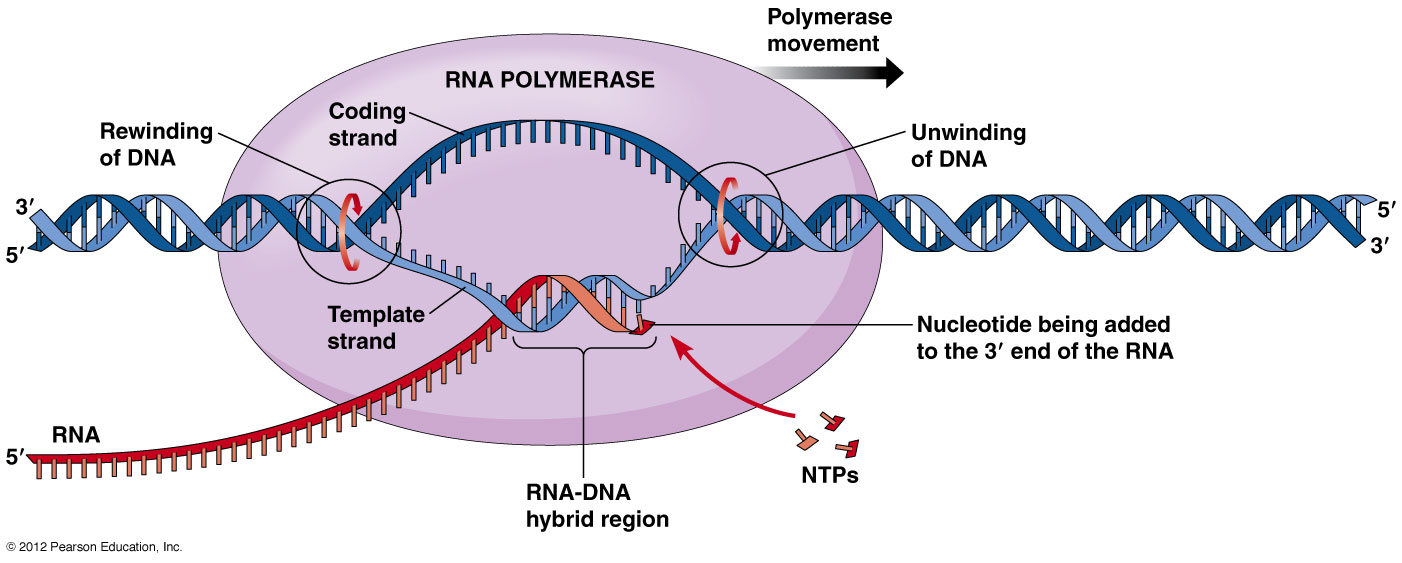
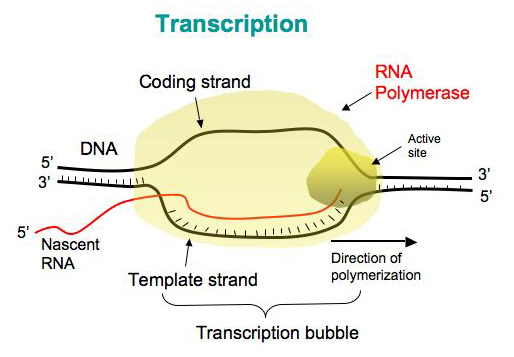
The DNA-dependent RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and catalyses the polymerization in the 5 to 3 direction on the template strand. Step 1 Bacteria Transcription. I This process is called Transcription in Prokaryotes.
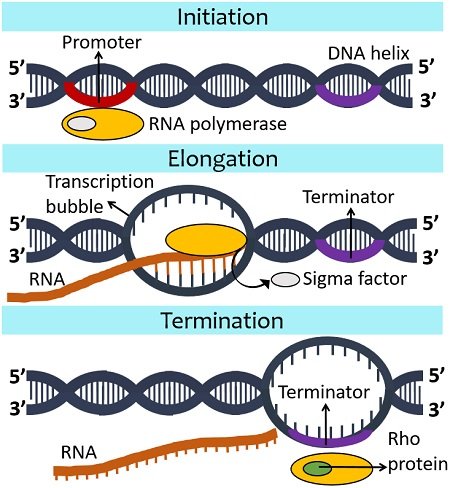
Initiation elongation and termination. Prokaryotic transcription also known as bacterial transcription is the process in which a segment of bacterial DNA is copied into a newly synthesized strand of messenger RNA mRNA which is later translated to produce proteins with the use of the enzyme RNA polymerase and other transcription factors. Elongation - When RNA polymerase moves from the promoter to the terminator site it causes the polymerisation of nucleoside triphosphate nucleotides resulting in the formation of RNA in the 5 - 3 direction.
View the full answer. The sigma sigma factor of RNA polymerase recognizes the promoter sequence in the double helix DNA. -10 and -35 regions binary complex closed complex core enzyme downstream sequences holoenzyme open-complex promoter sigma.
The RNA polymerase has co-factors β β α α and ω along with σ sigma factor that catalyse the process. Opens complex unwinds DNA to start. Transcription has three stepsinitiation elongation and termination.
RNA polymerase uses. Describe the process of initiation of transcription in bacteria. Describe the elongation process transcription in bacteria.
The high concentration of. RNA polymerase binds with the promoter to initiate the process of transcription. RNA polymerase selects NTP complementary to DNA template catalyzes phosphodiester bonds.
In prokaryotes the structural genes are polycistronic and continuous. The RNA chain is synthesized in the 5-3 direction. Transcription factors are up- down- and switched on in response to environmental signals in different ways.
Initiation The initiation of transcription in bacteria begins with the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter in DNA. Both bacterial transcription and translation occur simultaneously in the. The initiation begins with the RNA polymerase enzyme.
As bacteria are prokaryotic organisms the process is simple. Once the σ-factor binds the remaining subunits of the polymerase attach to the site. The RNA polymerase is the main enzyme involved in transcription.
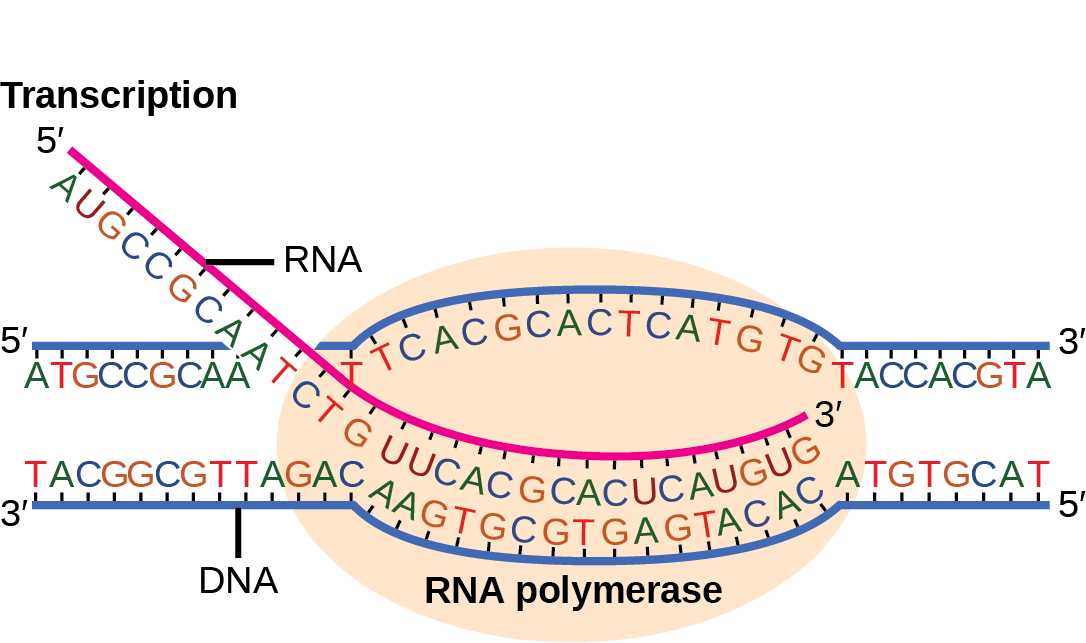
RNA polymerase uses one of the DNA strands the template strand as a template to make a new complementary RNA molecule. In bacteria transcription can be initiated only when sigma binds to the -35 and -10 boxes of the promoter in the DNA. Once it reaches the terminator sequence the process terminates and the.
3 Explain this process of transcription in prokaryotes. Transcription of a gene takes place in three stages. It causes the local unwinding of the DNA.
Transcription ends in a process called termination. At this point the holoenzyme is referred to as the closed complex. - Specific Binding Orientation.
Step 2 Bacteria Transcription. Iii RNA Polymerase bind to the promoter and initiates the process alongwith certain termination factors.
Prokaryotic Transcription Biology 2e

Describe The Process Of Transcription In Bacteria Biology Shaalaa Com

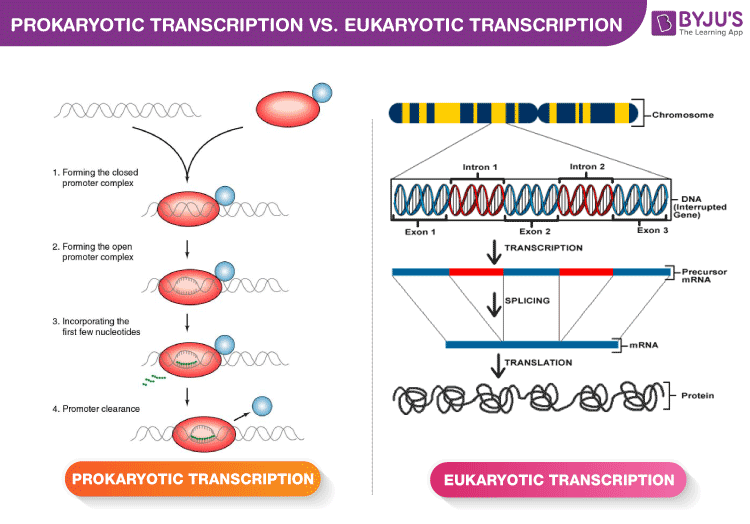
Difference Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Transcription Byju S
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy
What Is Bacterial Transcription Definition Key Terms Steps Biology Reader

Transcription In Prokaryotes Youtube
Explain The Transcription Process In Prokaryotes With Needed Diagram Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Prokaryotic Transcription Enzymes Steps Significance

The Bacterial Transcription Cycle Four Stages Promoter Recognition Download Scientific Diagram
Transcription In Prokaryotes Online Biology Notes
Prokaryotic Transcription Enzymes Steps Significance
Transcription In Prokaryotes Online Biology Notes
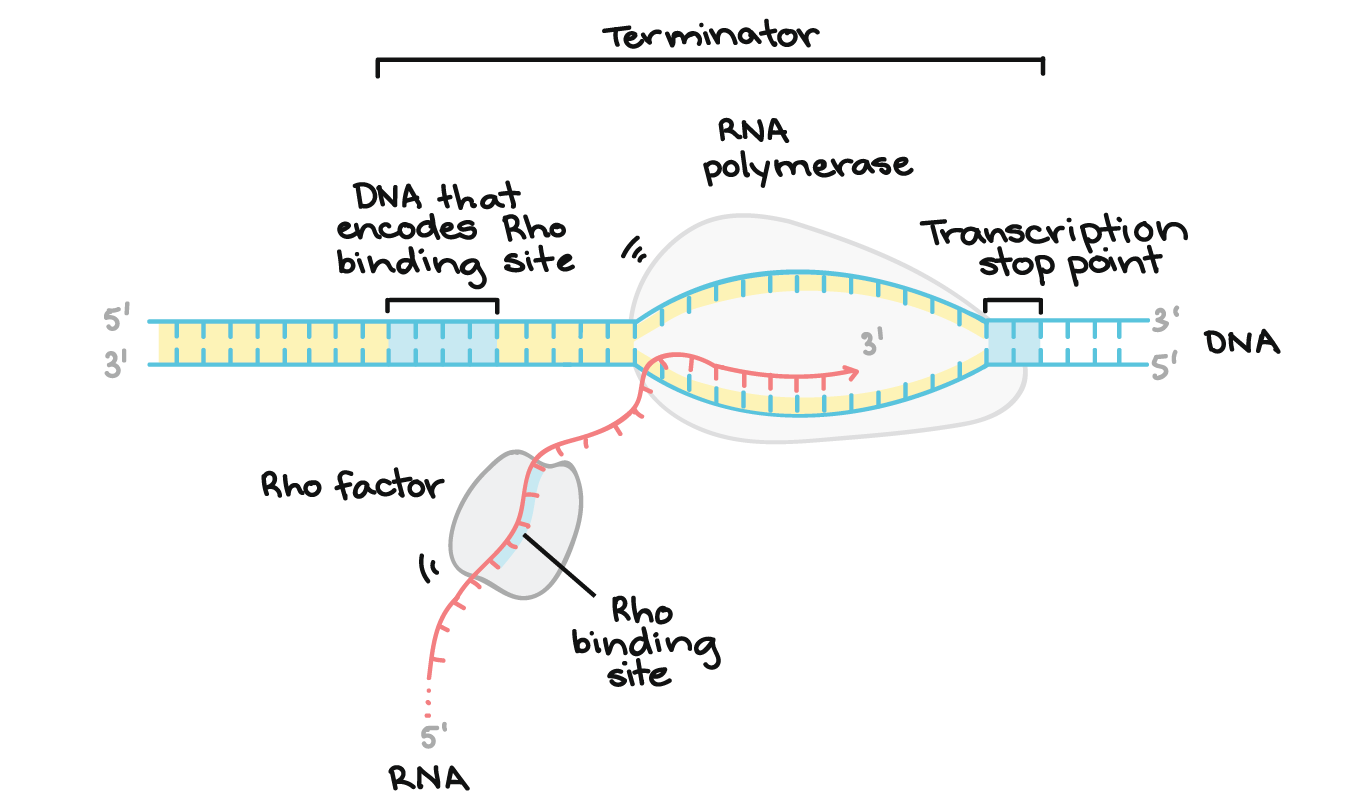
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy
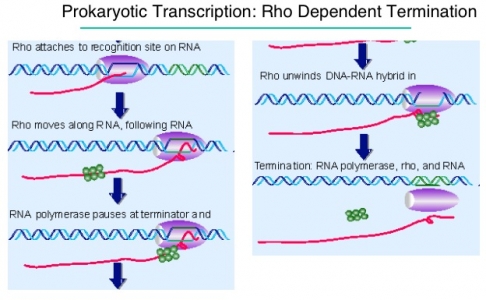
Transcription In Prokaryotes Online Biology Notes

Graphic Representation Of The Bacterial Transcription Process Download Scientific Diagram

Prokaryotic Transcription Biology For Majors I

Dna Transcription Learn Science At Scitable
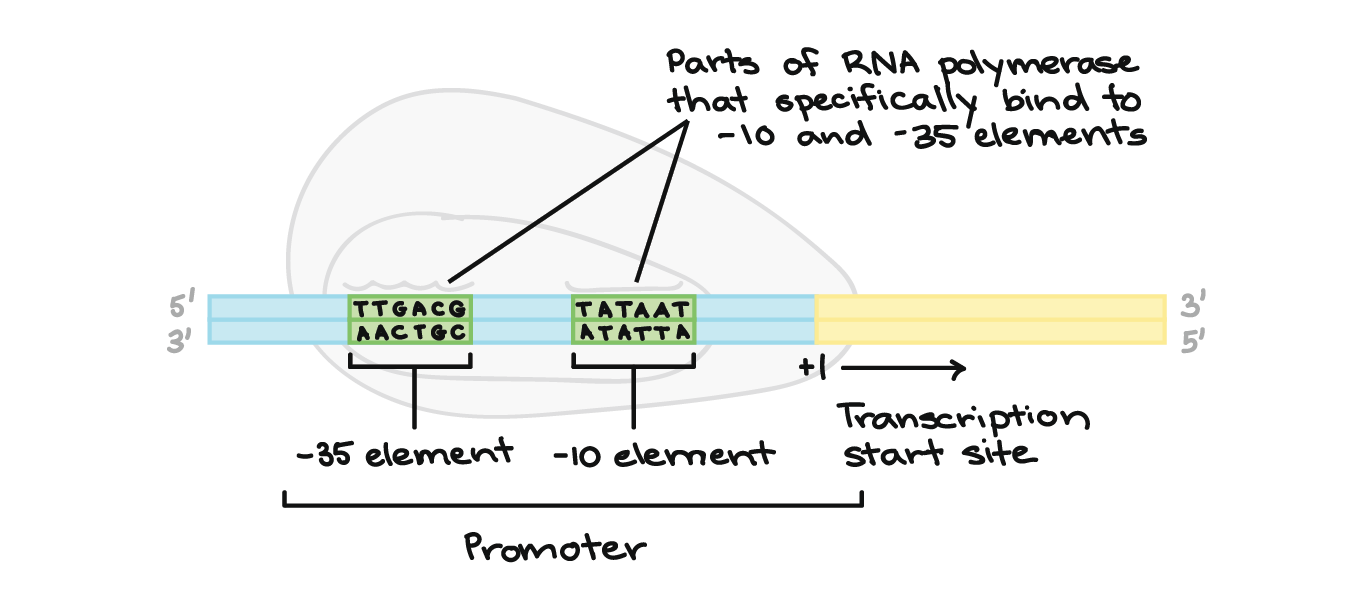
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy
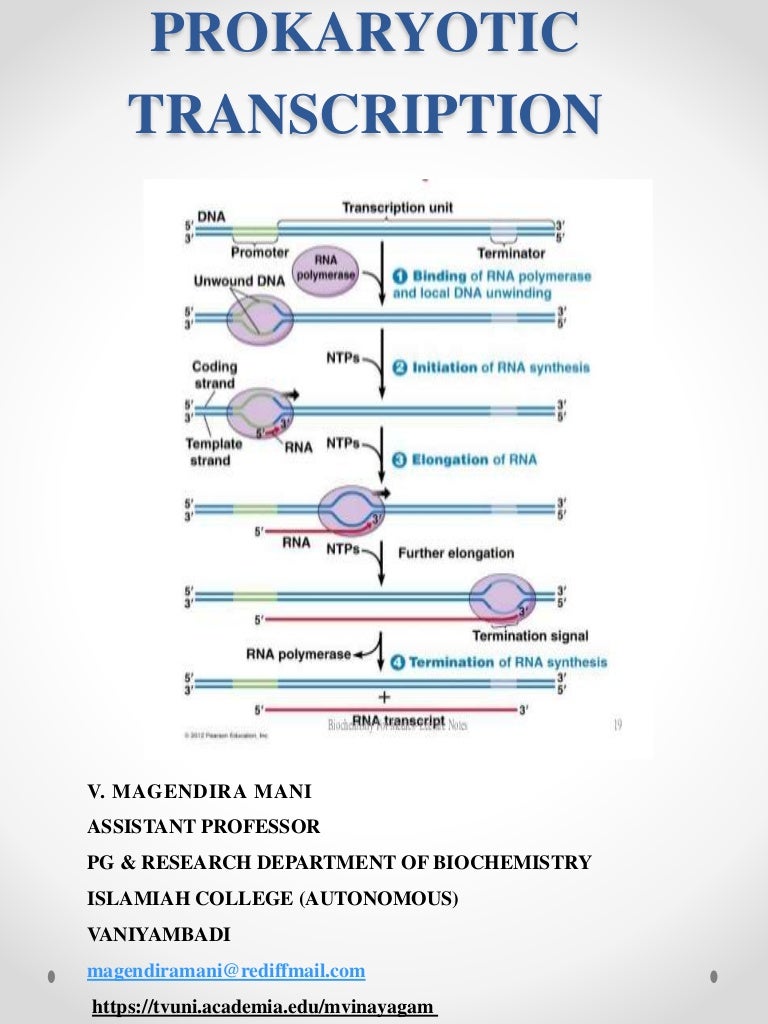
Comments
Post a Comment